I suggest that you type out the code yourself for each lesson. Doing so will better reinforce the lesson and help you commit the code to memory at a faster rate.
Download the workbook for this lesson
Without further delay, let’s jump into our first VBA program
This first program is going to be called Hello World. We are going to create a very simple program that contains just one line of code.
Open up a fresh Excel workbook, open up your IDE, and insert a module. Click here if you need a refresher on navigating to your IDE. In short, you can either navigate to your IDE through the Developer tab, or you can simply press ALT + F11.
Once you’ve got your IDE up and fresh module open, go ahead and type the following code. You can run the program by pressing F5, or by pressing the green play button in your IDE editor.
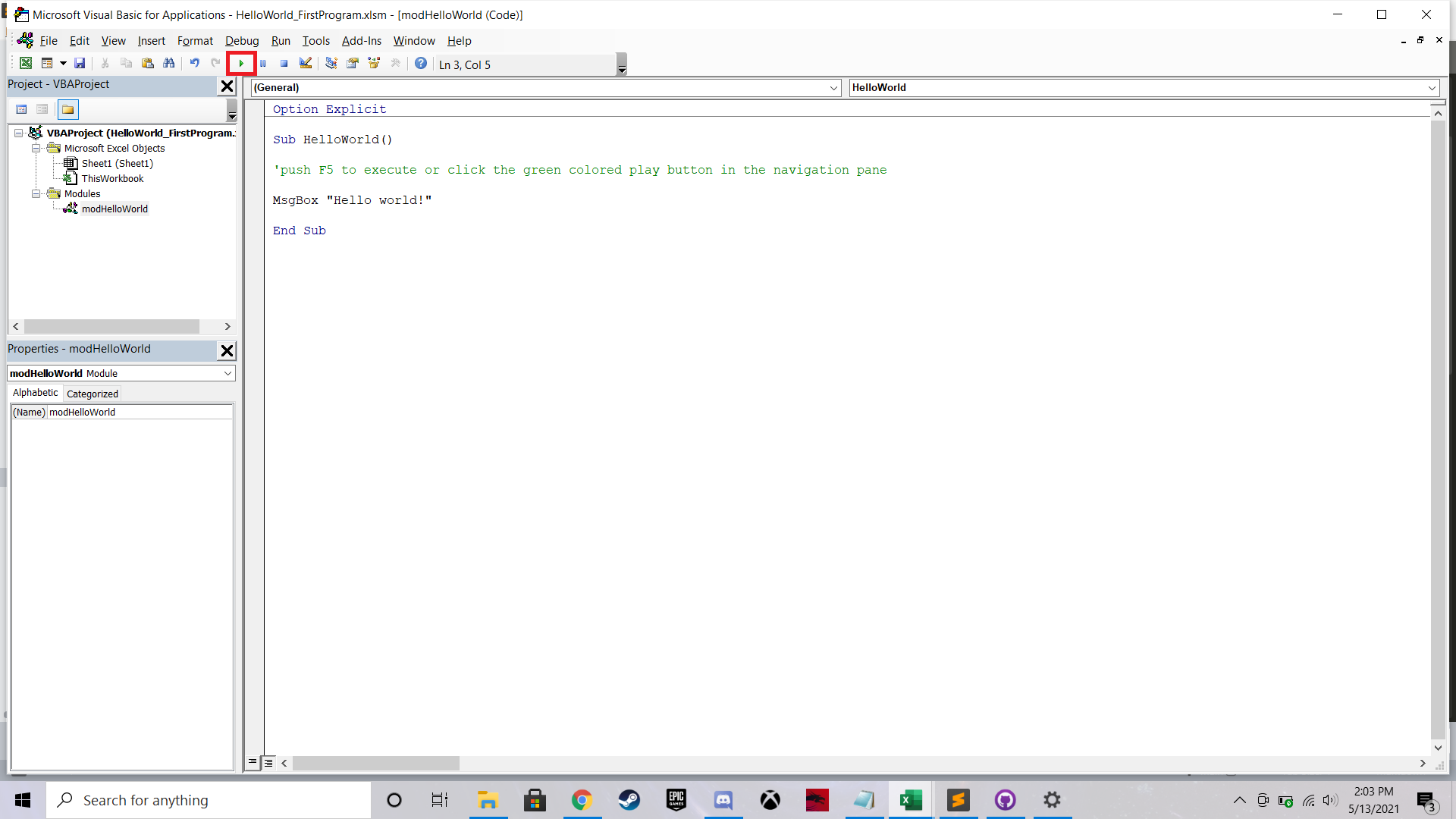
Option Explicit
Sub HelloWorld
'push F5 to execute or click the green colored play button in the navigation pane
MsgBox "Hello world!"
End Sub
What will the program do? The program is a very simple one. When you execute the code by pressing F5 or the play button, a message box will appear with the text “Hello World!” in it. When you press the “OK” button in the prompt, the program will end.
The Title
Sub HellWorld
*Code goes here*
End Sub
You start any software program using the keyword Sub followed by its program name. The program name has to be contiguous, with no spaces, nor can it start with a number. That’s why the HelloWorld is one word.
The End Sub appears automatically after you enter Sub program name and then press ENTER. You type your code between the title and End Sub.
Tips when titling a program
-
Create meaningful name The program name should be something that intuitively describes your program and what its intended purpose is.
-
Make it readable Capitalize the first letter in each world. It makes it so much more readable. If you have a program that parses text, for example, call it TextParser. Without the capitalizations, it would read as textparser which is harder to read.
Comments in code Comments in code are completely ignored by the compiler. This means that the VBA IDE will not recognize them as lines of executable code and will literally pass over them as if they don’t exist. Comments really help with keeping track of what your code does and where.
You create comments in code by using an apostrophe preceding a comment. You can see an example up above.
Lesson End
Take a moment to tinker this program. Add some comments for practice. Change the text from “Hello World” to something else. Get comfortable. The point of this very brief lesson was to illustrate where and how VBA is typed, and how to execute a program. Each lesson will build upon concepts from previous tutorials, so keep the lessons learned here in mind.
Navigation